With medical science and technology advancing at an increasingly rapid rate, it is more important than ever that doctors, nurses, and support staff stay up to date with continuing medical education. Continuing medical education (CME) can refer to educational activities which help to maintain and increase the knowledge, skills, and professional performance of medical health professionals. This can be in the form of formal courses, seminars, lectures, online classes, and workshops.
In this article, we examine the evolution of CME and current CME trends, investigating the shortcomings of the current methods and overcoming them by leveraging technologies such as telehealth cameras.
The Evolution of CME Delivery Methods

Over the years, CME has evolved from traditional, in-person lecture-based formats to dynamic, technology-enhanced learning experiences. Studies have shown live media to be more effective than print and multimedia formats more effective than single-media formats.
The ongoing advancement of educational research and technologies paves the way for more innovative and interactive delivery methods, including:
- Interactive online courses
- Webinars
- Multimedia content
- Virtual simulations
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR)
The Challenges for Medical Professionals

Despite the aforementioned advancements in CME, significant challenges in continuing medical education remain for medical professionals, highlighting the ongoing need for improvements to ensure and sustain physician competency and performance.
Professional Practice Gaps
According to the ACCME, a professional practice gap is defined as the "difference between current health care processes or outcomes observed in practice, and those potentially achievable on the basis of current professional knowledge”.
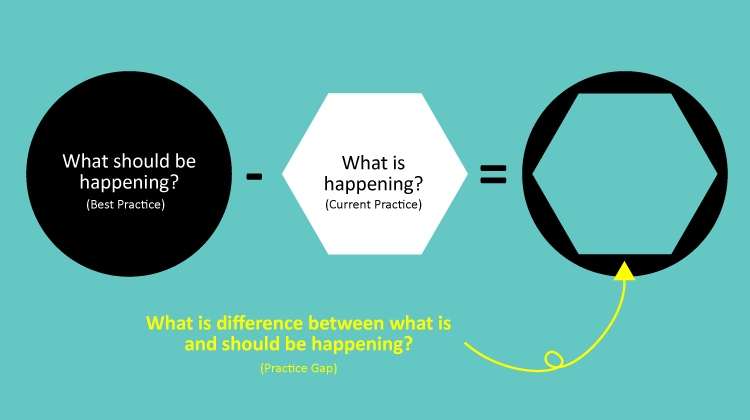
A practice gap can be categorized into one or more of the following types:
- Knowledge (does not know)
- Skill (does not know how)
- Practice (does not do)
Through performing gap analyses, medical professionals can effectively understand and begin to reduce the practice gap through CME, enabling the identification of areas for improvement and ultimately the achievement of improved patient care and safety.
Barriers to CME
Aside from practice gaps, medical professionals face many barriers to accessing Continuing Medical Education (CME). A 2021 survey with US clinicians indicates that expenses and travel time are the main barriers to CME, with 68% citing costs and 57% highlighting travel time as a significant concern.
With the existing barriers, medical professionals might be restricted from accessing the educational resources they need, thereby limiting their physician competency and performance.
“We should explore options that reduce barriers of time and money, and creatively use online tools to publicize new offerings.”
Bridging the Gap in CME with Telehealth Cameras
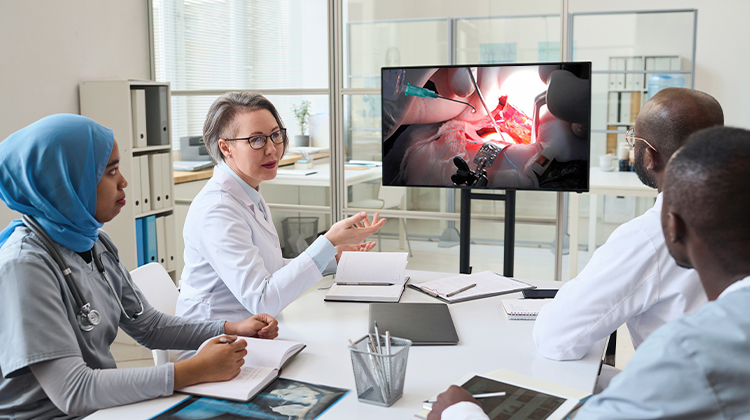

To solve the issues that medical practitioners face, CME has been moving online to improve accessibility, relying heavily on commercial general-use devices such as smart glasses and video conferencing cameras to satisfy the extensive demand for recording or streaming CME content. Medical professionals found several notable disadvantages when using these devices, including unstable image quality, the need for an additional audio device, and the inability to zoom in and capture the intended view. These limitations restricted the delivery of educational content.
When the pandemic struck, telehealth cameras were suddenly thrust to the forefront of the medical industry. Having undergone significant technological upgrades, telehealth cameras are being integrated into CME, most notably its use in surgical live-streaming, marking a pivotal shift in how medical education is delivered.
Applications of telehealth cameras in CME now include:
- Live Surgical Demonstrations – Telehealth cameras can stream live surgeries and procedures through high-quality video, allowing learners to observe techniques and ask questions in real-time, providing a first-hand learning experience.
- Recorded Sessions for On-Demand or Online Learning – Telehealth cameras can record educational sessions with high image quality, making them available for on-demand or online viewing. This supports self-paced learning and revisiting complex topics.
- Remote Workshops and Training – They enable the conduct of interactive workshops such as medical simulation training where participants can practice clinical skills under the guidance of experts, even from remote locations.
Telehealth cameras connect CME participants with specialists and experts worldwide, providing guidance and knowledge that may not be locally available, offering flexibility in scheduling, and helping to reduce learning costs.
Revolutionizing Continuing Medical Education
As medical science progresses, the importance of continuing medical education (CME) becomes increasingly evident. However, traditional methods of CME delivery often pose significant barriers to accessibility and effectiveness for medical professionals. In response to these challenges, the integration of telehealth cameras into CME represents a transformative step forward. By leveraging telehealth technology, medical practitioners can access high-quality educational content in real-time, participate in interactive workshops remotely, and collaborate with experts worldwide, ultimately enhancing their knowledge, skills, and patient care abilities. As we continue to harness the power of technology, it is crucial to prioritize innovative approaches to CME delivery, ensuring that healthcare professionals remain equipped to meet the evolving demands of modern medicine.
Explore how AVer’s Connected Health Solutions offer a win-win for everyone involved and the future of CME.